
INDONESIA LIQUEFIED NATURAL GAS (LNG) MARKET
Natural gas is a fossil fuel majorly comprising of methane. As with other fossil fuels, it is formed deep beneath the earth’s surface due to the decomposition of dead plants and animals under extreme heat and pressures. Natural gas is cleaner than most other fossilized fuels. However, its calorific value is lower than the fossil fuels like petrol, diesel, and LPG.
To learn more about this report, request a free sample copy
Indonesia accounted for more than one-third of the total global LNG exports in the 1990s. In 2020, Indonesia’s share in the global market was merely 4.4%. Indonesia exported about 593 Bcf (Billion cubic feet) of LNG in the same year, going upward from 582 Bcf in 2019. The country has become a regional supplier, exporting LNG to countries like South Korea, Japan, and China.
Since the last 40 years, Indonesia has become quite an important liquefied natural gas (LNG) player. The domestic LNG demand in the country saw a continuous growth rate at a fast pace in line with the robust economic growth outlook and the upcoming initiation of more gas-fired power plants. The total proved reserves of the country as of 2020 are 2.4 trillion cubic meters. This forms 0.3% of the global total proved reserves.
At the same time, the exports related to LNG have been falling due to its low demand domestically and expiring contracts with the buyers from overseas. Multiple new projects are already scheduled to maintain and boost Indonesia’s gas and LNG output.
Also, there are certain areas where transportation using pipelines is impossible, and liquefying natural gas is how transportation can be cost-effective. The natural gas is cooled to about -260 degrees Fahrenheit to form Liquefied Natural Gas, i.e., LNG. The volume reduction is to the tune of 600 times the original.
The oil industry in Indonesia dates back to the 19th century, where the first oil was discovered in the North Sumatra region in 1885. The gas industry had started its operations in 1863, along with the introduction of town gas manufactured from coal to light the streets of Jakarta city.
Indonesia has been considered one of the first producers of LNG, with the first project commissioned in 1977. Since the late 1970s, the country’s economy had benefited from higher oil prices used for its exports.
The Government of Indonesia has estimated that the domestic LNG demand would offset natural gas exports by 2028, when the country would become a net importer. All gas exports would be ceased by 2034. Also, the government has made further announcements about pipeline gas exports to be stopped to Singapore by 2023 and focus on the domestic market. As per the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (MEMR), this diversion in the supply to Singapore would be mainlined into the pipeline of Dumai Duri transmission, which would be later administered to several industrial estates in the Sumatra region.
Since LNG is highly flammable and major exporting takes place by the sea, many regulations are to be followed by the industry players. Key regulatory authorities that govern the LNG industry in the country are National Energy Policy, Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (MEMR), and Directorate General for Oil and Gas (DGOG).
The top LNG companies in the country are BP Berau Ltd, Pertamina, Medco, etc.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below:
We offer 10% free customization including country-level data, niche applications and competitive landscape with every report.
- INDONESIA LNG MARKET: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- INDONESIA OVERALL ECONOMIC CONDITIONS
- INDONESIA PRIMARY ENERGY CONSUMPTION
- NATURAL GAS
- INDONESIA NATURAL GAS TOTAL PROVED RESERVES, PRODUCTION, AND CONSUMPTION
- TOTAL PROVED RESERVES
- NATURAL GAS PRODUCTION
- NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION
- INDONESIA NATURAL GAS TOTAL PROVED RESERVES, PRODUCTION, AND CONSUMPTION
- LIQUIFIED NATURAL GAS (LNG)
- VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- EXPLORATION AND PRODUCTION
- LIQUEFACTION
- SHIPPING
- STORAGE AND REGASIFICATION
- END-USERS
- TRADE
- EXPORTS
- IMPORTS
- LNG TERMINALS
- LIST OF LNG EXPORT TERMINALS
- LIST OF LNG IMPORT TERMINALS
- REGULATORY FRAMEWORK FOR LNG
- VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 1: INDONESIA NATURAL GAS TOTAL PROVED RESERVES, 2000, 2010, AND 2020 (IN TRILLION CUBIC METERS)
TABLE 2: INDONESIA NATURAL GAS PRODUCTION, 2016-2020 (IN EXAJOULES)
TABLE 3: INDONESIA NATURAL GAS CONSUMPTION, 2016-2020 (IN EXAJOULES)
TABLE 4: INDONESIA LNG EXPORTS, 2016-2020 (IN BILLION CUBIC METERS)
TABLE 5: INDONESIA LNG IMPORTS, 2016-2020 (IN BILLION CUBIC METERS)
TABLE 6: LNG EXPORT TERMINALS, EXISTING
TABLE 7: LNG IMPORT TERMINALS, EXISTING
TABLE 8: REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE 1: INDONESIA GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT, 2016-2020 ($ BILLION)
FIGURE 2: PRIMARY ENERGY CONSUMPTION, BY FUEL TYPES, 2019 & 2020 (IN %)
FIGURE 3: PRIMARY ENERGY CONSUMPTION, 2016-2020 (EXAJOULES)
FIGURE 4: INDONESIA NATURAL GAS PRODUCTION VS CONSUMPTION, 2016-2020 (IN EXAJOULES)
FIGURE 5: VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
INDONESIA GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT, 2016-2020, ($ BILLION)
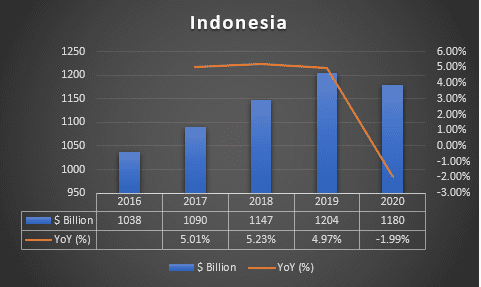
GDP (constant 2010 US$)
Source: World Bank
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below :
We offer 10% free customization including country-level data, niche applications and competitive landscape with every report.
